Full-stack
DevOps
The concept of DevOps focuses on integrating development (Dev) and operations (Ops) to optimize the software development lifecycle. With DevOps, companies can improve deployment efficiency, scalability, and monitoring of their applications. In this chapter, we will explore some key tools in the DevOps realm, such as Docker and Kubernetes, which help teams effectively manage applications in production environments.
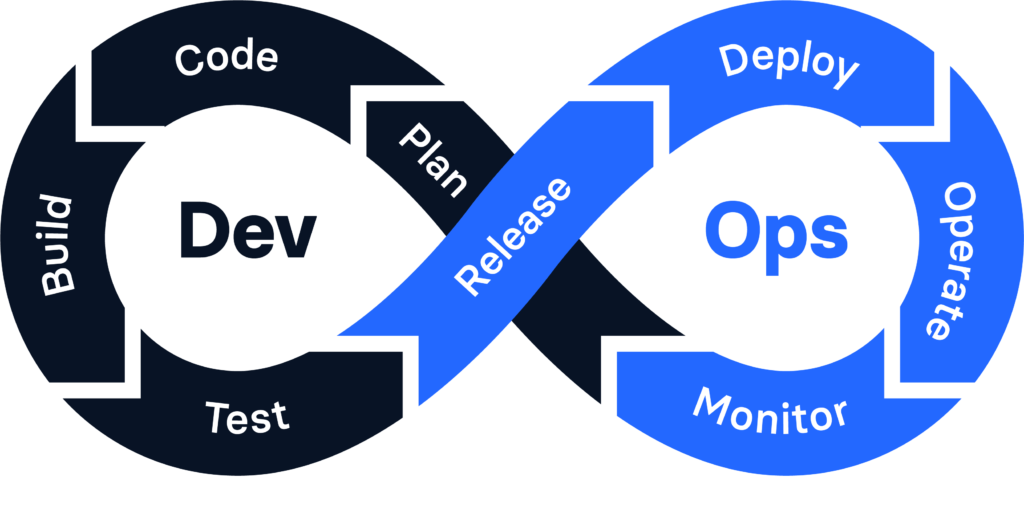 This image shows the DevOps lifecycle, which includes development, testing, deployment, and monitoring in a continuous cycle
This image shows the DevOps lifecycle, which includes development, testing, deployment, and monitoring in a continuous cycle
Docker: Containers for Application Deployment
Docker is a container platform that allows you to package applications and their dependencies into lightweight and portable containers. Containers facilitate deployment across different environments without worrying about configuration differences.
Example of a basic Dockerfile for a Node.js application:
dockerfile
Kubernetes: Container Orchestration
Kubernetes is an orchestration platform that automates the management of containerized applications at scale. With Kubernetes, you can distribute and manage multiple containers in a cluster environment, ensuring high availability and scalability.
Basic example of a YAML file to deploy an application in Kubernetes:
yaml
Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD)
One of the key practices in DevOps is Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD), which allows automating the process of code integration and deployment of new versions. This reduces downtime and enables the rapid and efficient release of new features.
Monitoring and Maintenance
In addition to deployment, DevOps includes tools for monitoring and maintaining applications in production. Platforms like Prometheus and Grafana allow DevOps teams to collect metrics and create visualizations, helping in early problem detection and decision-making to improve performance.
Conclusion
Integrating DevOps into full stack development enables the creation of more stable, scalable, and maintainable applications. Through tools like Docker and Kubernetes, developers can manage and deploy applications with efficiency and precision.
In the next and final chapter, we will explore various tools that facilitate daily work in development, including Git and other useful terminal commands.
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck














