Progressive Web Apps with HTML5 (PWA)
Performance Optimization in Progressive Web Apps
Performance is a crucial aspect in the development of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs). A well-optimized PWA not only enhances the user experience but also contributes to the overall success of the application by reducing load times and improving interaction. In this chapter, we will explore tools and strategies to optimize the performance of your PWA.
Why is performance optimization important?
A slow application can frustrate users, leading to lower retention and conversion rates. PWAs, with their ability to work offline and offer fast load times, should leverage optimization strategies to ensure a smooth experience.
Using Lighthouse to Audit Performance
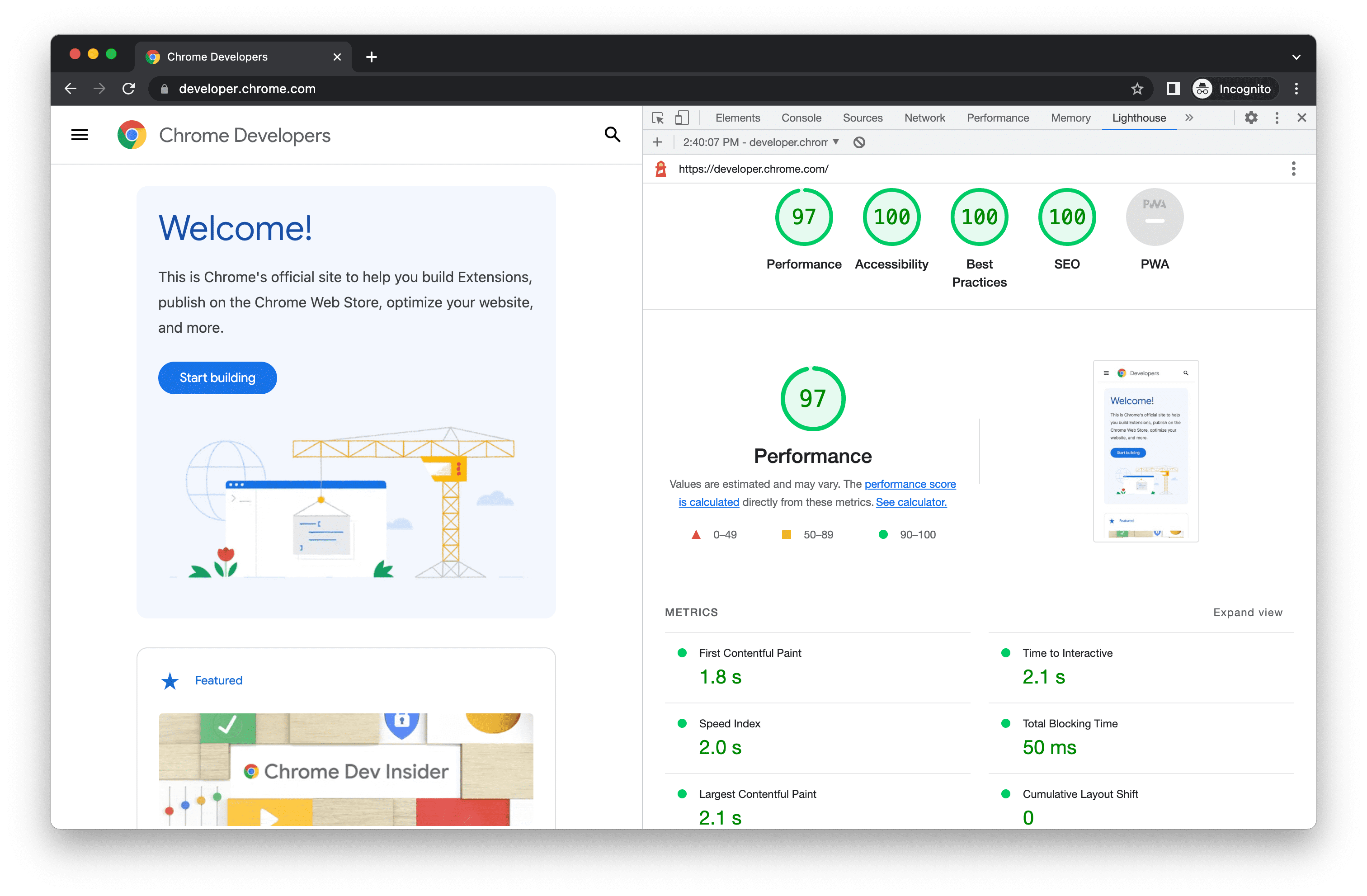
Lighthouse is a tool built into Chrome DevTools that allows you to evaluate and optimize the performance of PWAs. It provides detailed reports on key metrics such as load time and interactivity.
Steps to use Lighthouse
- Open your PWA in the Google Chrome browser.
- Go to the developer tools (DevTools) and select the "Lighthouse" tab.
- Configure the audit by selecting "Progressive Web App" and "Performance."
- Click "Generate Report" to start the audit.
Key metrics in Lighthouse
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): Measures the time it takes for the browser to render the first visible content.
- Time to Interactive (TTI): Evaluates the time until the application is fully interactive.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Indicates the time at which the page's largest content element is rendered.
Optimization Strategies
Minimization and Compression of Files
Reducing the size of your PWA's files can significantly speed up load times. Use tools like:
- Minifiers: Tools like UglifyJS and CSSNano remove unnecessary spaces and comments in your files.
- Gzip or Brotli Compression: Configure the server to compress files before sending them to the client.
Technical Example: Gzip Configuration on Nginx
nginx
Using Lazy Loading
Lazy loading delays the loading of resources that are not immediately needed, such as images that are outside the user's initial view.
Technical Example: Lazy loading in images
html
Implementing Efficient Cache Strategies
Besides the strategies covered in previous chapters, ensure to combine strategies like Stale While Revalidate to balance speed and content updates.
JavaScript Optimization
The size and execution of JavaScript scripts can significantly impact your PWA's performance. To optimize them:
- Split the code into smaller modules (code splitting).
- Use tree-shaking to eliminate unnecessary code.
- Load scripts asynchronously or deferred.
Technical Example: Loading scripts with defer
html
Performance Testing on Different Devices
It is important to test your PWA on a variety of devices and connections to ensure consistent performance.
- Use simulators in DevTools to emulate low-power devices.
- Test slow connections using throttling mode in DevTools.
Conclusion
Optimizing the performance of a PWA is essential to ensure fast load times and a high-quality user experience. Using tools like Lighthouse, cache strategies, and techniques like lazy loading and compression can make a significant difference. In the next chapter, we will explore advanced PWA features such as push notifications and background synchronization. Keep going to learn more!
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck

- Introduction to Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
- Core Concepts of Progressive Web Apps
- Setting Up Your First Progressive Web App
- Service Workers in Depth
- The Manifest File of PWAs
- Offline Functionality in Progressive Web Apps
- Performance Optimization in Progressive Web Apps
- Advanced Features in Progressive Web Apps
- Deploying and Distributing Your Progressive Web App
- Integration of PWAs with Other Web APIs
- Debugging and Testing Progressive Web Apps
- The Future of Progressive Web Apps
- Conclusion of the Progressive Web Apps Course













