HTML Forms
Form Submission and Data Handling
Once a form has been completed, the next step is to send the data to the server for processing. In this chapter, we will explore the methods of data submission in HTML, how to handle data on the server, and some security recommendations when working with forms.
Form Submission Methods: GET and POST
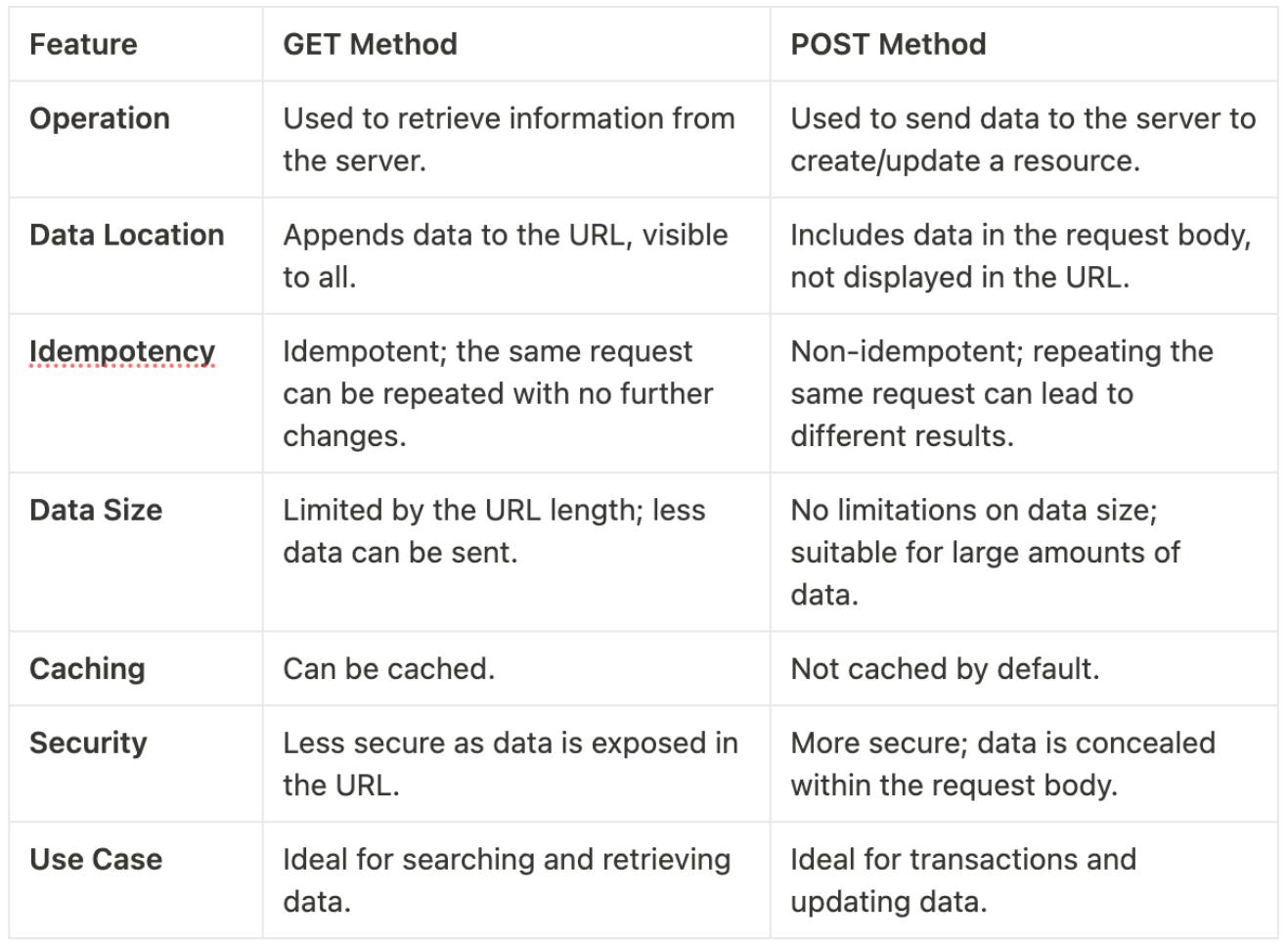
HTML allows two main methods for submitting data: GET and POST. Each method has specific uses and affects how the data is transmitted.
- GET: Sends data as part of the URL. It's suitable for searches and non-sensitive data since the data is visible in the address bar.
- POST: Sends data in the HTTP request body, which is more secure for sending sensitive data like passwords or personal information.
html
html
Sending Forms to an API
It is common to send form data to an API instead of directly to an HTML server. Using JavaScript, you can make an asynchronous request with fetch or XMLHttpRequest to send the data to the API and process the response.
Example of Sending Data with fetch
html
target Attribute
The target attribute in the <form> tag defines where the form response will be opened. It can be useful for opening the result in a new tab or a specific iframe.
html
Receiving and Handling Data on the Server
When the server receives form data, it can process it in various ways. Data submitted via POST is usually handled in the request body, while data sent via GET is handled as URL parameters.
Example in Node.js
In this example, a Node.js server receives form data using the express package.
javascript
HTML Form Security
It is critical to implement security measures to protect data and prevent attacks. Some recommendations include:
- Server-side validation: Validation in the browser is useful, but it should always be complemented with server-side validation to prevent tampering.
- Avoid exposing sensitive data: Data like passwords should never be sent using the
GETmethod. - Protection against injection attacks: Ensure to sanitize input data to avoid code injection attacks.
Example of Server-side Validation
javascript
Chapter Conclusion
In this chapter, we covered methods for submitting form data, handling data on the server, and some security recommendations. In the next chapter, we will explore how to style HTML forms using CSS, enhancing usability and visual design to provide an optimal user experience.
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck

- Introduction to HTML Forms
- HTML Form Elements
- Attributes and Controls in HTML Forms
- Validation and Constraints in HTML Forms
- Advanced HTML Form Elements
- Form Submission and Data Handling
- Styling HTML Forms with CSS
- Best Security Practices in HTML Forms
- Interactive and Dynamic Forms
- Best Practices and Common Errors in HTML Forms
- Conclusion of the HTML Forms Course













