HTML5 Geolocation API
Requesting User Location and Managing Permissions
Now that we have a basic understanding of what the Geolocation API is, it's time to delve into how to effectively request the user's location. In this chapter, we'll explore how to handle user consent, the methods to obtain location, and how to manage common errors that might arise.
Understanding User Consent
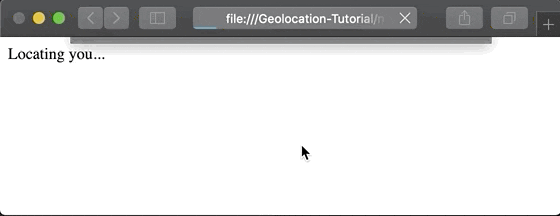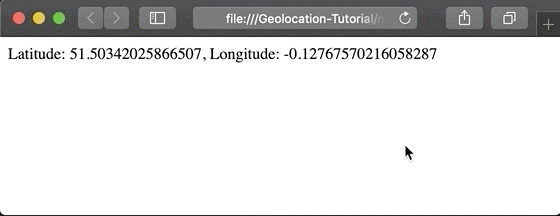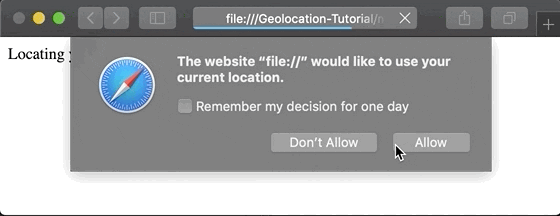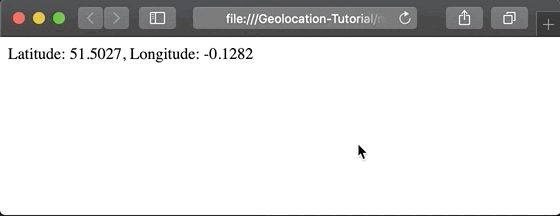
Since location is sensitive information, web browsers are designed to protect user privacy. This means that whenever an application attempts to access location, the browser presents an alert requesting permission. Only after the user grants this permission can the application access their position.
It is crucial to respect user consent and employ good practices, such as explaining why their location is needed in the user interface. This can improve the acceptance rate of permissions and provide greater transparency.
Using getCurrentPosition to Obtain the Current Location
To request the user's location, the getCurrentPosition method of the Geolocation API is the simplest and most common option. This method attempts to obtain the user's current location once and can be handled as follows:
javascript
Implementation Example of getCurrentPosition
Suppose we want to display the latitude and longitude on the screen once the user grants permission. We can write the following code:
javascript
Handling Common Errors
The Geolocation API can return different errors when trying to access the user's location. These errors are identified by specific codes:
- 1 - PERMISSION_DENIED: the user declined the location request.
- 2 - POSITION_UNAVAILABLE: the location could not be obtained due to a device or network problem.
- 3 - TIMEOUT: the location request took too long to respond.
To handle these errors, the error callback function can use a control structure to display custom messages depending on the error type.
javascript
Practical Implementation: Requesting Location on Page Load
Sometimes, it is useful to ask for the user's location immediately after loading the page, for example, in a maps or local recommendation application. We can achieve this by calling the showPosition function within the DOMContentLoaded event.
javascript
Best Practices for Requesting Permissions
Requesting the user's location appropriately and ethically helps build trust. Here are some recommended practices:
- Explain Location Usage: Clearly and transparently indicate how the location will be used.
- Offer Alternatives: If the user does not grant permission, offer an option to manually enter a location or continue without this feature.
- Avoid Frequent Requests: Request location only when necessary to avoid annoying the user.
- Provide Settings Options: Allow the user to disable or adjust location access in the application preferences.
These best practices are especially important in applications that continuously use geolocation.
Chapter Summary
In this chapter, we explored how to request user location using the getCurrentPosition method, as well as handle permissions and address common errors. These tools are essential to ensure a smooth and reliable user experience when implementing the Geolocation API. In the next chapter, we will see how to continuously track user location with the watchPosition method, ideal for real-time applications such as navigation.
Let's move forward and learn how to track user location in real time!
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck

- Introduction to the Geolocation API
- Requesting User Location and Managing Permissions
- Retrieving Location Coordinates
- Advanced Options in Geolocation
- Handling Errors in the Geolocation API
- User Movement Tracking with `watchPosition`
- Integration of Geolocation with Maps
- Practical Project: Geofencing Implementation
- Troubleshooting Common Problems in Geolocation
- Conclusion and Next Steps













