Basic CSS
Use animations and transitions in an accessible manner
Animations and transitions in CSS can enhance the user experience when used correctly. However, it is important to ensure that they do not interfere with accessibility. In this chapter, you will learn how to use animations and transitions in a way that is not intrusive and how to ensure they do not negatively affect users with disabilities.
 User shown in motion
User shown in motion
Benefits and risks of animations
Animations can make the user interface more dynamic and engaging. However, they can also be problematic for people with certain types of disabilities, such as those who suffer from dizziness, vertigo, or photosensitive epilepsy.
Best practices for accessible animations
- Avoid fast or abrupt movements: Animations that move elements quickly or unpredictably can cause dizziness.
- Reduce the duration of animations: Long or prolonged animations can distract users.
- Respect user preferences: Some users configure their devices to reduce or eliminate animations. Your site should respect those preferences.
Use the prefers-reduced-motion query
The prefers-reduced-motion media query allows you to detect if a user has enabled a preference to reduce motion in their operating system. You can use this query to disable or simplify animations and transitions when necessary.
Example of prefers-reduced-motion
css
Keep animations non-intrusive
Animations should be subtle and not disrupt the user experience. For example, effects involving flickering or fast color changes should be avoided, as they can be distracting or uncomfortable.
Example of a subtle animation
css
Limit animation repetition
Animations that repeat indefinitely can distract users. Be sure to limit animations to a reasonable number of repetitions or disable them after a certain time.
Example of animation with repetition limit
css
Smooth and accessible transitions
Transitions are a great way to enhance the user experience, especially if they are used to smooth state changes, such as when hovering or interacting with buttons.
Example of smooth transition
css
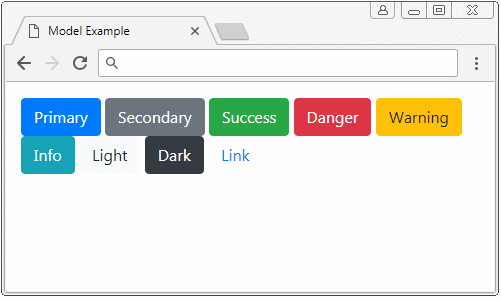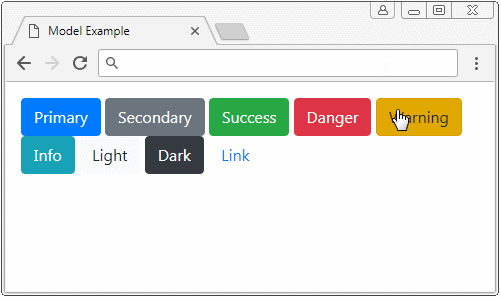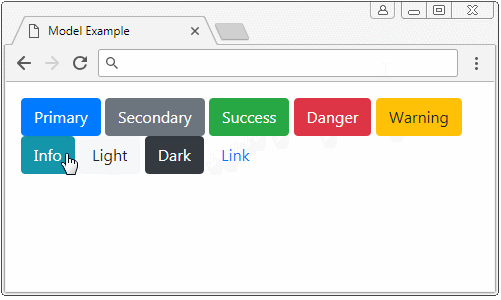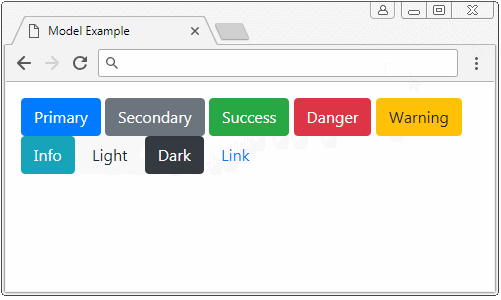 Buttons animation shown here
Buttons animation shown here
Avoid flicker or rapid color changes
Flickering or rapid color changes can trigger seizures in certain users with photosensitive epilepsy. Ensure that no element on your page flickers or changes color more than three times per second.
Example of safe flicker
css
Respect the user's timing
Some transitions and animations, like image carousels or pop-up messages, can automatically advance. It's important to give users control over these automatic transitions so they can interact at their own pace.
Example of carousel control
html
Tools to test the accessibility of animations
There are several tools you can use to verify the accessibility of animations and transitions on your website:
- Lighthouse: A Google tool that audits the accessibility of a website, including animations.
- axe Accessibility Checker: It also allows you to check if animations meet accessibility standards.
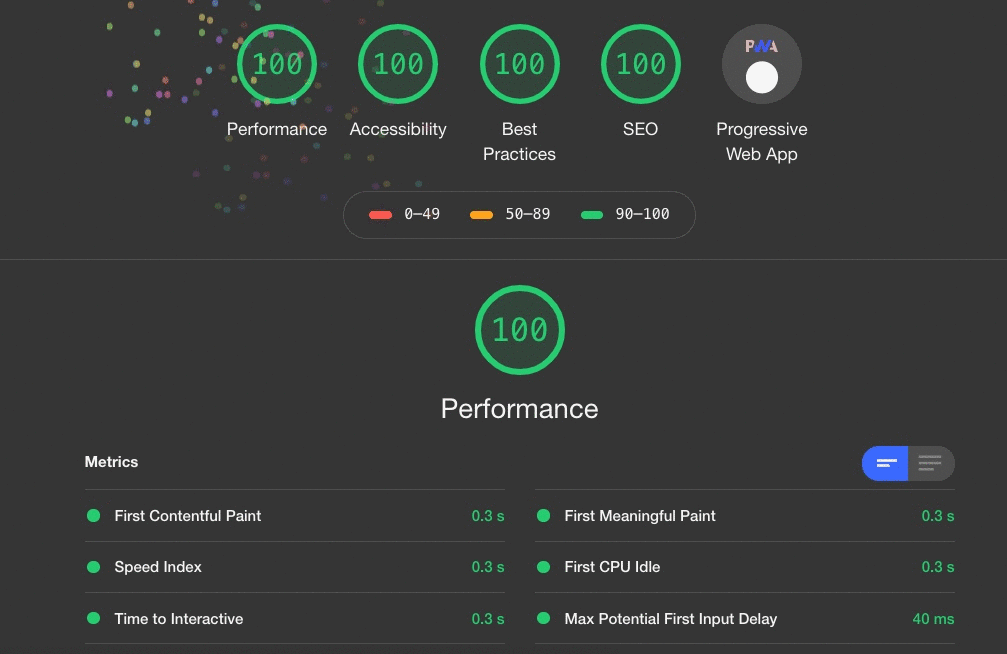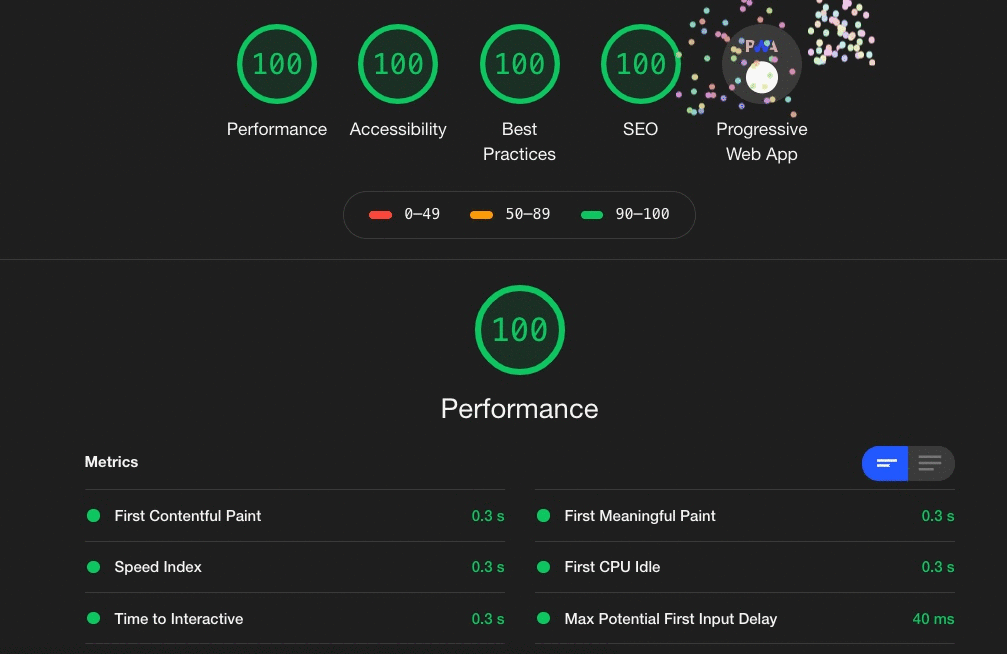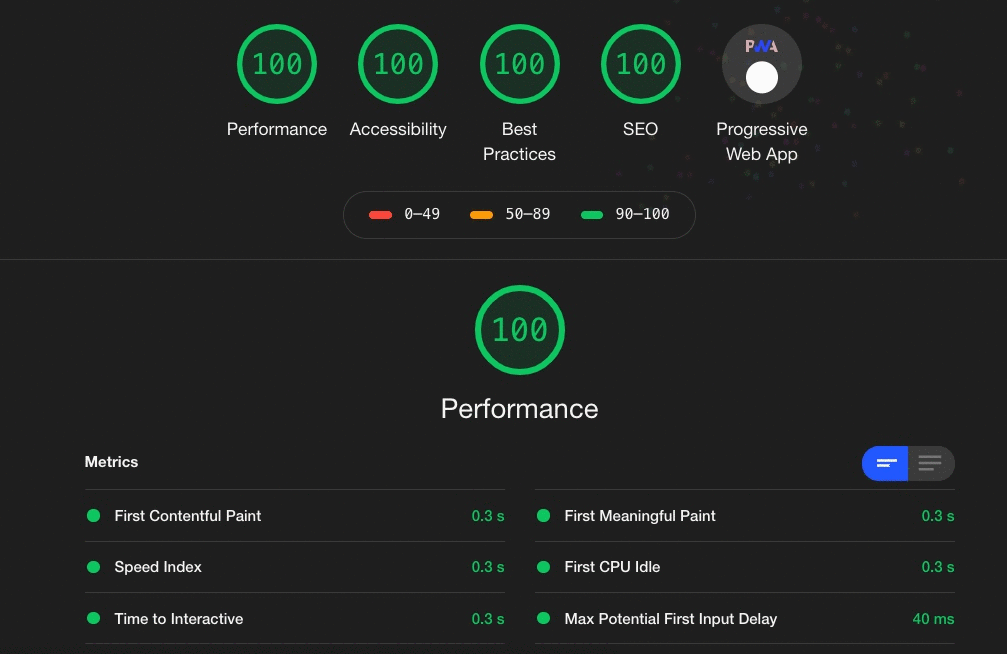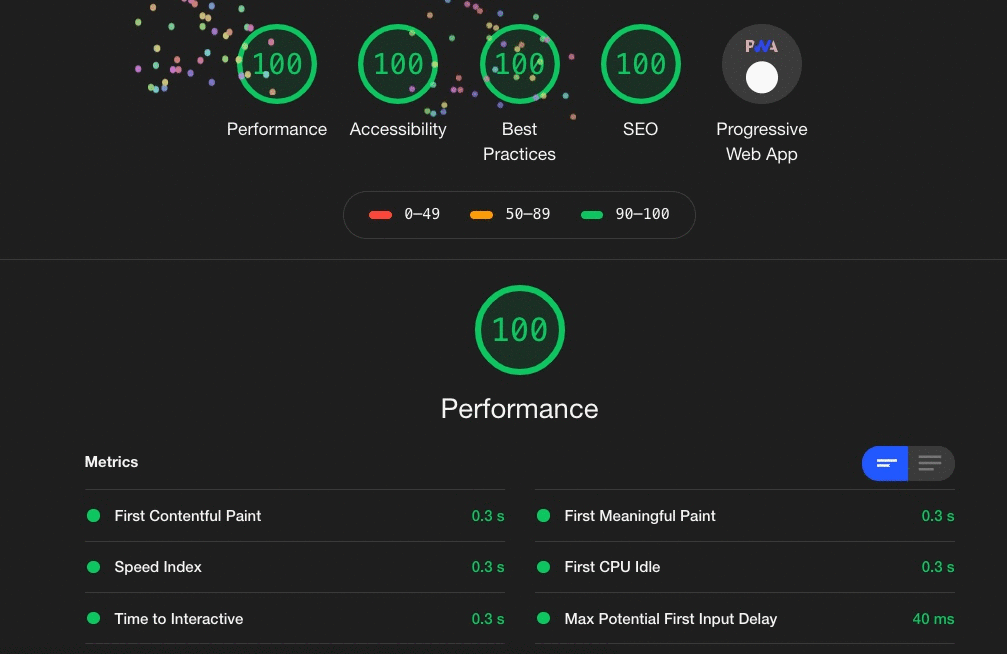 Screenshot of an accessibility audit performed with Lighthouse is shown here.
Screenshot of an accessibility audit performed with Lighthouse is shown here.
Conclusion
In this chapter, you have learned how to use animations and transitions in an accessible way, ensuring they do not interfere with the experience of users who may be sensitive to motion or flicker. By implementing best practices such as limiting motion, respecting user preferences, and keeping animations smooth and subtle, you can improve the accessibility of your website. In the next chapter, we will explore how to optimize CSS performance for large and complex sites.
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck

- Introduction to CSS
- CSS Selectors
- The Box Model in CSS
- Colors and Backgrounds in CSS
- Typography in CSS
- Design Techniques with CSS
- Responsive Design Fundamentals in CSS
- Responsive Navigation in CSS
- Responsive Forms in CSS
- Combinando CSS con HTML para un diseño completo
- CSS Debugging and Optimization
- Working with CSS Libraries and Frameworks
- Customizing CSS Frameworks
- Structuring Large CSS Projects
- Best Practices for CSS Performance
- Keeping CSS Code Clean and Well-Documented
- Testing and Debugging CSS
- Ensuring Accessibility with CSS
- Use animations and transitions in an accessible manner
- CSS Optimization for Large Websites
- Keeping Clean and Scalable CSS Code













