Basic CSS
CSS Debugging and Optimization
It is important not only to write CSS correctly but also to keep your code clean and efficient. In this chapter, you will learn techniques to debug issues in your CSS and optimize it to improve your web page's performance.
Identifying and Resolving Issues in CSS
One of the biggest challenges when working with CSS is identifying and fixing issues when the style isn't applied as expected. Next, we will look at some strategies for debugging CSS.
Using the Browser's Developer Tools
Modern browsers have built-in tools that allow you to inspect elements of a webpage and see which styles are being applied. To open the developer tools in most browsers:
- Google Chrome / Firefox: Right-click on a page element and select "Inspect".
In the "Elements" tab, you can view the HTML of your page, and in the "Styles" section, you can see which CSS rules are affecting the selected element.
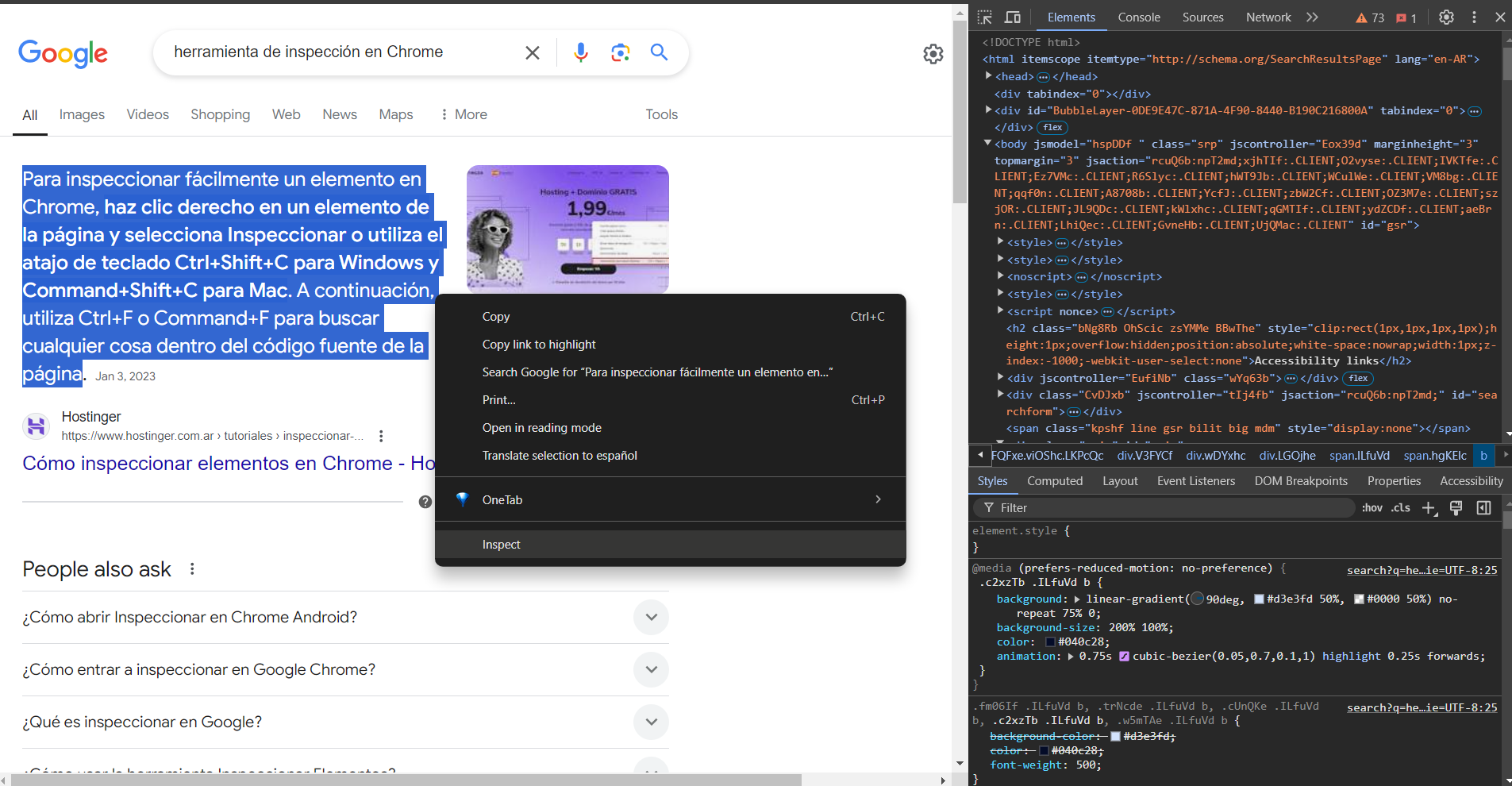 This image shows a screenshot of the inspection tool in Chrome displaying the HTML
This image shows a screenshot of the inspection tool in Chrome displaying the HTML
Checking the Cascade and Specificity
In CSS, rules are applied based on the cascade and specificity. If a style isn't applied as expected, it may be due to another rule with higher specificity taking precedence. Specificity depends on the selectors used in the style rule.
- ID selectors (
#my-id) have more specificity than class selectors (.my-class). - Type selectors (
div,p) have less specificity than class and ID selectors.
If you find that a CSS rule is not having an effect, you can increase its specificity or use the developer tool to see which rule is prevailing.
css
Using !important
If you want to force a CSS rule to take precedence over all others, you can use !important. However, use it sparingly, as it can make future debugging difficult.
css
CSS Validation Tools
To ensure your CSS is error-free, you can use validation tools. The W3C CSS Validator is one of the most widely used tools for detecting errors in your CSS code.
- Visit W3C CSS Validator and paste your CSS or provide your website's URL to validate your code.
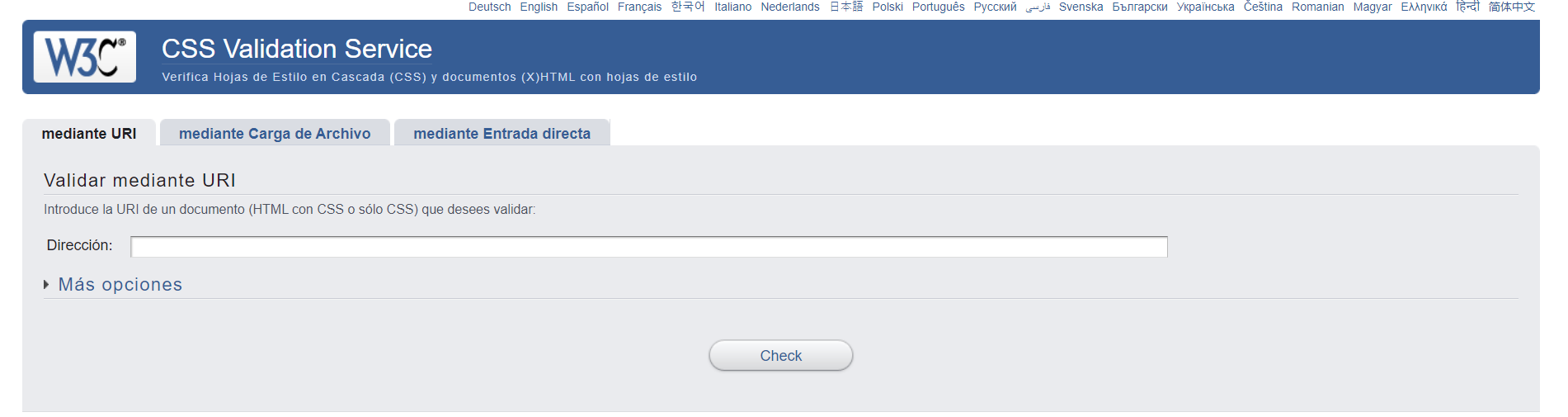 This shows the W3C CSS Validator tool
This shows the W3C CSS Validator tool
CSS Performance Optimization
As you add more styles to your website, your CSS file size may grow, affecting performance. Below are some strategies to optimize your CSS.
CSS Minification
Minification is the process of removing all unnecessary spaces, line breaks, and comments from your CSS file to reduce its size. This doesn't affect functionality but does reduce load time.
css
Removing Unused CSS
Sometimes, there may be CSS rules that are not applied to any page element. These unnecessary rules increase the file size. You can use tools like PurgeCSS or UnCSS to remove unused CSS.
Grouping CSS Rules
Grouping CSS rules that share similar properties can also help reduce file size and make it easier to maintain.
css
Efficient CSS Structuring
Keeping your CSS file well-organized is crucial, especially in larger projects. Here are some tips to structure your CSS efficiently:
-
Use comments to separate sections and make reading easier.
css -
Divide your CSS into multiple files if necessary, for example, one for overall layout, another for colors, and another for responsive design.
-
Use clear naming conventions, like BEM (Block, Element, Modifier), to maintain consistency in class names.
css
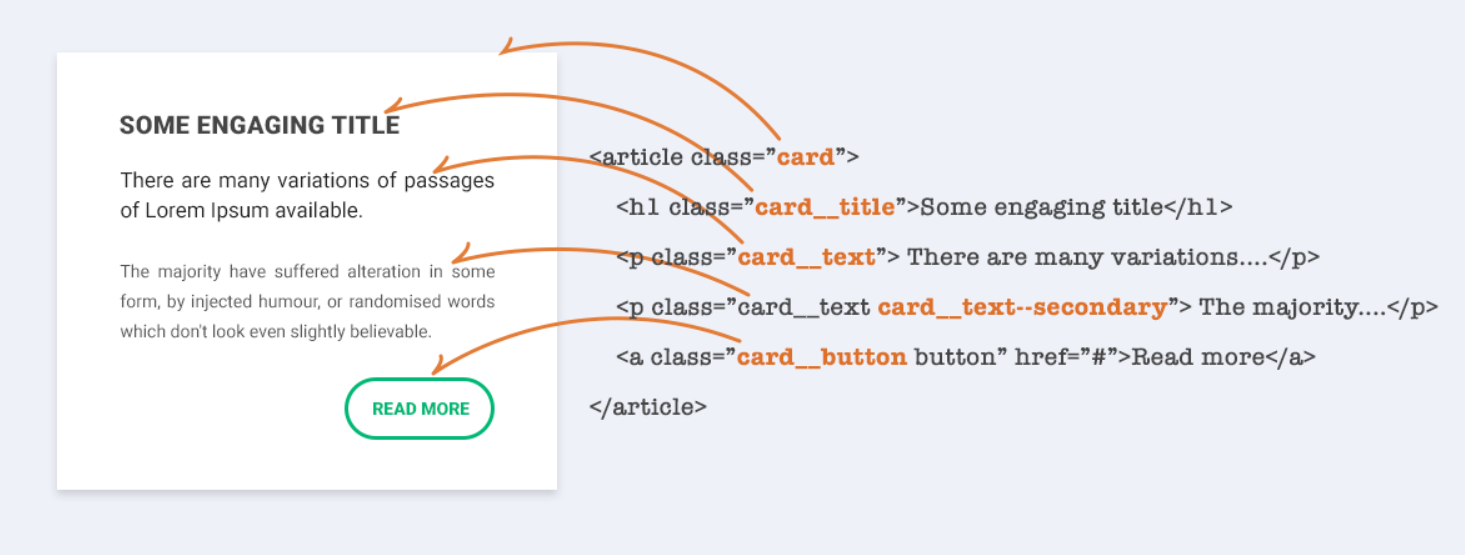 This image shows how to structure a CSS file using conventions like
This image shows how to structure a CSS file using conventions like
Conclusion
In this chapter, you learned how to debug your CSS using the browser's developer tools, identify specificity issues, and use CSS validation tools. We also explored strategies to optimize your CSS and improve your website's performance. In the next chapter, we will look at how to work with CSS libraries and frameworks to streamline the development of larger projects.
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck

- Introduction to CSS
- CSS Selectors
- The Box Model in CSS
- Colors and Backgrounds in CSS
- Typography in CSS
- Design Techniques with CSS
- Responsive Design Fundamentals in CSS
- Responsive Navigation in CSS
- Responsive Forms in CSS
- Combinando CSS con HTML para un diseño completo
- CSS Debugging and Optimization
- Working with CSS Libraries and Frameworks
- Customizing CSS Frameworks
- Structuring Large CSS Projects
- Best Practices for CSS Performance
- Keeping CSS Code Clean and Well-Documented
- Testing and Debugging CSS
- Ensuring Accessibility with CSS
- Use animations and transitions in an accessible manner
- CSS Optimization for Large Websites
- Keeping Clean and Scalable CSS Code













