Docker
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) with Docker
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) are fundamental practices for automating the development, testing, and deployment of applications. Docker integrates well with CI/CD tools, facilitating the implementation of automated pipelines to efficiently build, test, and deploy containers.
Introduction to CI/CD
Continuous Integration (CI) is a process that ensures code changes are regularly integrated and tested. Continuous Delivery (CD) allows these changes to be automatically deployed to production or testing environments, reducing development time and minimizing errors.
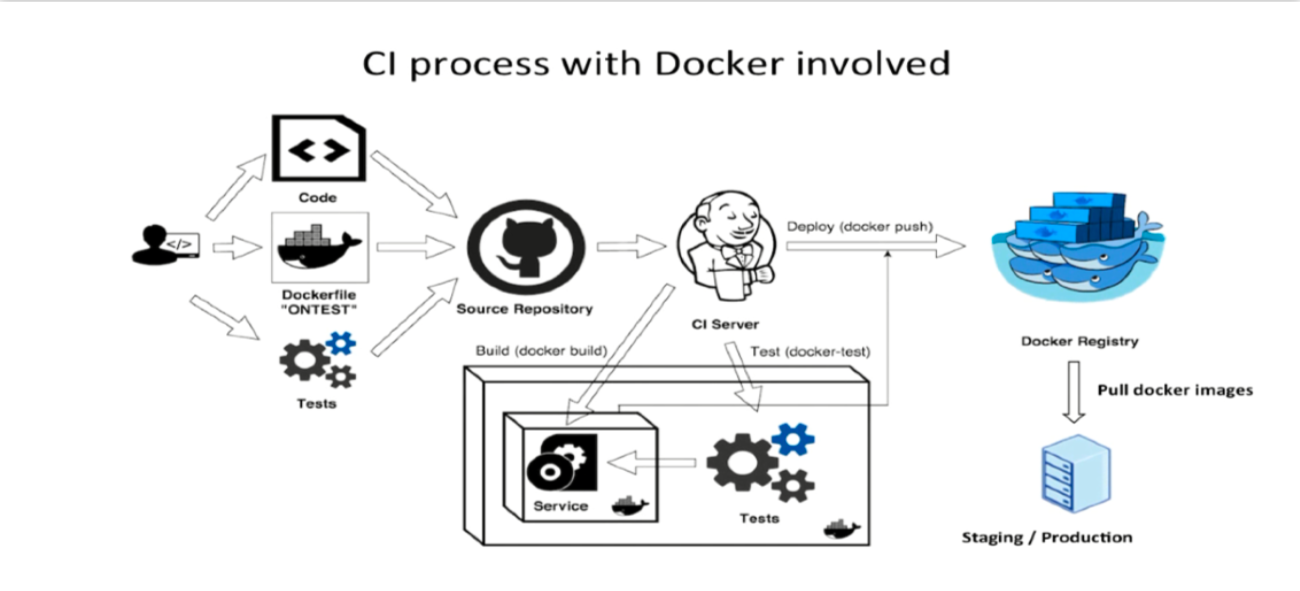
CI/CD Tools for Docker
There are multiple CI/CD tools that support Docker. Some of the most popular include:
- Jenkins: An extensible automation platform that allows integrating Docker to build and deploy images.
- GitLab CI/CD: Integrated tool in GitLab for creating pipelines and automating deployments.
- GitHub Actions: Offers workflows that enable automating CI/CD tasks directly from GitHub.
Create a Basic CI/CD Pipeline with Docker
Below is an example of configuring a CI/CD pipeline using a YAML file for GitLab CI/CD.
Example of a .gitlab-ci.yml File
This file defines a basic pipeline that builds a Docker image, runs tests, and deploys the image to an environment.
yaml
Automated Building and Testing with Docker
Automated testing ensures code quality before deployment. Docker facilitates running tests in containers, ensuring that the environment is consistent.
Example of Testing with Docker
To run tests inside a Docker container, include the necessary dependencies and scripts in the image.
dockerfile
Automated Container Deployment
In a CI/CD pipeline, the deployment stage ensures that approved changes are automatically deployed to the production or testing environment.
Example deployment command:
bash
Conclusion
Implementing CI/CD with Docker accelerates the development cycle and allows reliable and efficient continuous delivery. With automated build, test, and deployment pipelines, teams can release versions quickly and with quality. In the next chapter, we will explore Docker image registry and how to manage them in Docker Hub and other registries.
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck

- Introduction to Docker and Containerization
- Installation and Configuration of Docker
- Principles of Containers and Virtualization
- Images in Docker: Creation and Management
- Writing and Optimizing Images
- Volumes and Persistent Storage in Docker
- Networking in Docker: Container Connectivity
- Docker Compose: Multi-Container Application Management
- Best Practices in Docker for Application Deployment
- Resource Management and Optimization in Docker
- Security in Docker and Best Containerization Practices
- Docker Swarm: Basic Container Orchestration
- Kubernetes vs Docker Swarm: Introduction to Kubernetes
- Deployment and Scalability with Kubernetes
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) with Docker
- Docker Image Registry: Docker Hub and Alternatives
- Monitoring and Logging of Containers in Docker
- Problem Solving and Debugging in Docker
- Migrating Applications to Docker Containers
- Practical Examples: Deploying Web Applications and APIs
- Conclusions and Best Practices in Using Docker













