Docker
Problem Solving and Debugging in Docker
As you work with Docker in development and production environments, you're likely to encounter issues that require debugging techniques. In this chapter, we will explore tools and methods to diagnose and resolve common problems in Docker containers.
Diagnosing Containers with Docker Inspect
The docker inspect command provides detailed information about a container's configuration and state. This information is useful for verifying configurations and detecting connectivity or permission issues.
bash
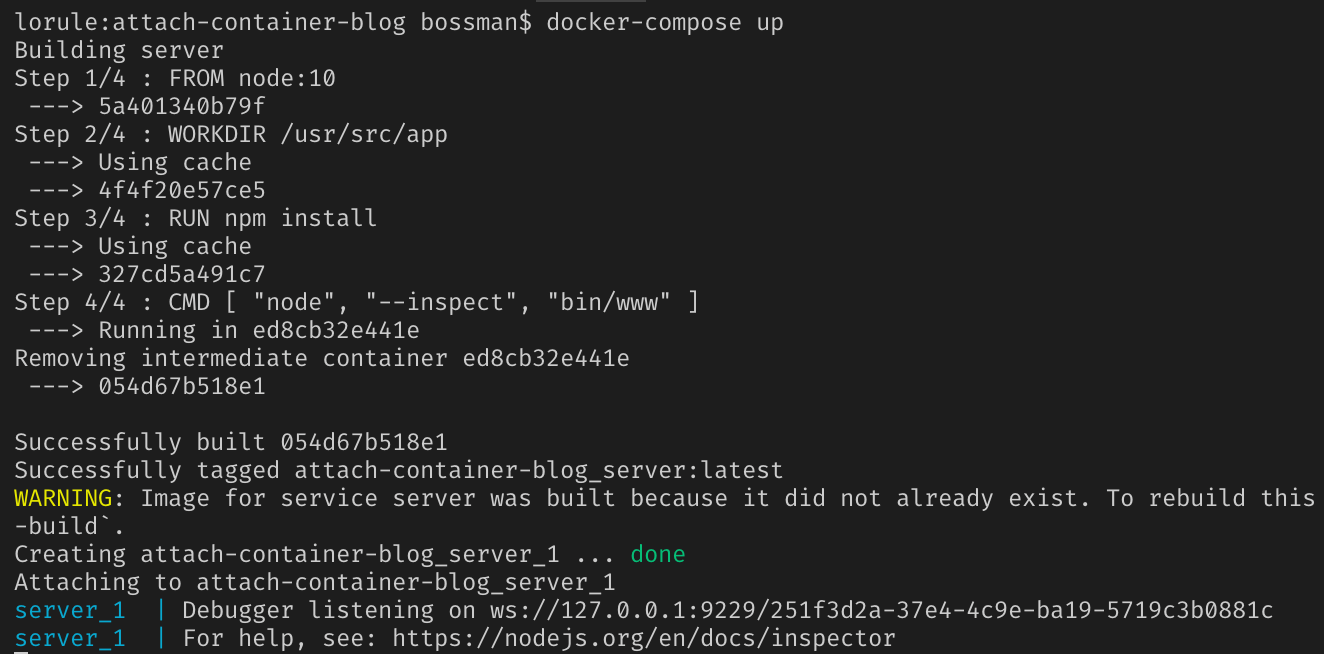 This image shows how docker inspect works
This image shows how docker inspect works
Accessing a Running Container
To inspect the internal environment of a container, Docker allows access to the command line of a running container. This is useful for examining files, reviewing logs, and executing commands directly within the container.
bash
Viewing Logs in Real Time
Accessing a container's logs is crucial to understanding the application's behavior and detecting errors. Docker allows viewing logs in real time, facilitating the monitoring of events in the container.
bash
Inspecting Network Connections
Docker allows inspecting the network configuration of containers to troubleshoot connectivity issues. The docker network inspect command shows the configuration of a network and the containers connected to it.
bash
External Debugging Tools
In addition to Docker's internal tools, there are external tools that can help diagnose and debug containerized applications.
- cAdvisor: Monitors resource usage of containers and provides data on CPU, memory, and network.
- Netshoot: Docker image with network tools that facilitate troubleshooting connectivity issues between containers.
- GDB (GNU Debugger): Allows debugging applications in low-level languages like C/C++.
Example of Using Netshoot for Network Issues
To solve connectivity issues between containers, use the nicolaka/netshoot image which includes network diagnostic tools.
bash
Debugging Images and Build
During the build of an image, issues with dependencies and configurations may arise. Docker allows building images in debug mode and reviewing each layer to identify the problem.
Running in Interactive Mode
During the build of an image, you can use RUN in interactive mode to execute commands and verify configurations at each step.
dockerfile
Conclusion
The ability to diagnose and resolve issues in Docker is essential for maintaining application stability and performance. With the tools and techniques presented in this chapter, developers can efficiently tackle common problems.
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck

- Introduction to Docker and Containerization
- Installation and Configuration of Docker
- Principles of Containers and Virtualization
- Images in Docker: Creation and Management
- Writing and Optimizing Images
- Volumes and Persistent Storage in Docker
- Networking in Docker: Container Connectivity
- Docker Compose: Multi-Container Application Management
- Best Practices in Docker for Application Deployment
- Resource Management and Optimization in Docker
- Security in Docker and Best Containerization Practices
- Docker Swarm: Basic Container Orchestration
- Kubernetes vs Docker Swarm: Introduction to Kubernetes
- Deployment and Scalability with Kubernetes
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) with Docker
- Docker Image Registry: Docker Hub and Alternatives
- Monitoring and Logging of Containers in Docker
- Problem Solving and Debugging in Docker
- Migrating Applications to Docker Containers
- Practical Examples: Deploying Web Applications and APIs
- Conclusions and Best Practices in Using Docker













