Express JS
Express Fundamentals

In this chapter, we will explore the fundamental concepts of Express. We will see how to handle routes, use middlewares, and work with HTTP requests and responses. Understanding these fundamentals is essential for building robust and scalable applications with Express.
Routes in Express
One of the most important tasks in any web application is handling routes. Routes in Express are used to define how the application should respond when it receives a request at a specific URL. Each route can handle different types of HTTP requests such as GET, POST, PUT, or DELETE.
Defining Basic Routes
Let's see how to define some basic routes in Express:
javascript
Routes with Parameters
Express allows us to define dynamic routes that can receive parameters in the URL. These parameters are useful when we need to respond to specific requests based on some value passed in the URL.
javascript
Middleware in Express
In the previous chapter, we briefly mentioned the concept of middleware in Express. Now we will delve into its use.
What is a Middleware?
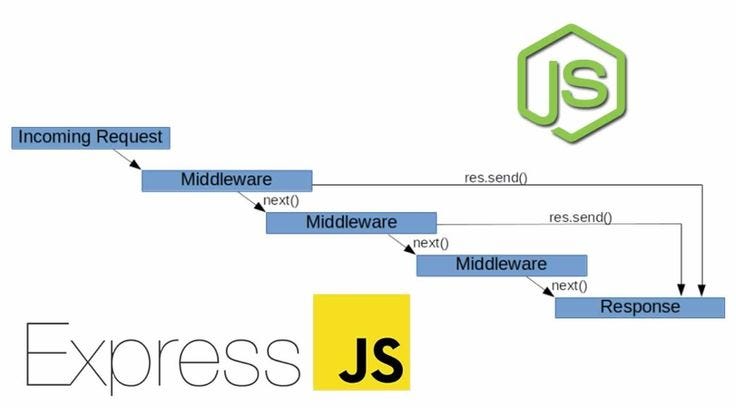
A middleware is essentially a function that executes during the request lifecycle in an Express application. It has access to the request object (req), the response object (res), and the next function, which indicates when to pass control to the next middleware.
Middlewares can be used to perform various tasks, such as authentication, data validation, activity logging, or error handling.
Using Middlewares
To use middleware in Express, we can use the app.use() function. Here is an example of a simple middleware that logs the URL of each request:
javascript
Middlewares are powerful because they allow adding functionalities to requests without directly modifying the routes.
Third-Party Middlewares
Express also supports third-party middlewares, which are external packages that can be installed and used in the application. Some examples include body-parser for parsing JSON request bodies or cookie-parser for handling cookies.
We can install a middleware like body-parser and use it to parse JSON data in a POST request.
bash
Then, we can use this middleware in our application:
javascript
Requests and Responses in Express
In Express, handling requests and responses is a central part of any web application. An HTTP request has several components, and Express allows us to work with this data easily.
Accessing Request Data
HTTP requests contain several important data that we can use in our application, such as parameters, headers, and the request body. Here we show how to access some of this data.
javascript
Sending Responses
Express provides several methods for sending responses. The most common is res.send(), but we can also use res.json() to send JSON format responses, or res.status() to send HTTP status codes along with a response.
javascript
javascript
Conclusion
In this chapter, we have explored some of the most important fundamentals of Express, such as handling routes, using middlewares, and managing requests and responses. These concepts are essential for any developer looking to build robust and efficient applications with Express.
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck

- Introduction to Express JS
- Express Fundamentals
- Request and Response Management
- Estructura de Proyectos en Express
- Authentication and Authorization in Express
- Connecting Express with Databases
- Error Handling and Logging in Express
- Sending Emails in Express
- Security in Express Applications
- Advanced Middleware in Express
- Creating REST APIs with Express
- WebSocket Implementation in Express
- Implementation of Webhooks in Express
- Testing Express Applications
- Deployment of Express Applications
- Performance Optimization in Express
- Monitoring and Maintenance of Express Applications
- Best Practices and Scalability in Express
- Course Conclusion: Express JS













