Express JS
Advanced Middleware in Express
Middlewares are one of the most powerful and flexible components of Express. They allow us to intercept requests and responses throughout an application's lifecycle, giving us the ability to extend functionalities such as authentication, data validation, activity logging, and much more. In this chapter, we will delve into advanced middlewares and how to create custom middleware.
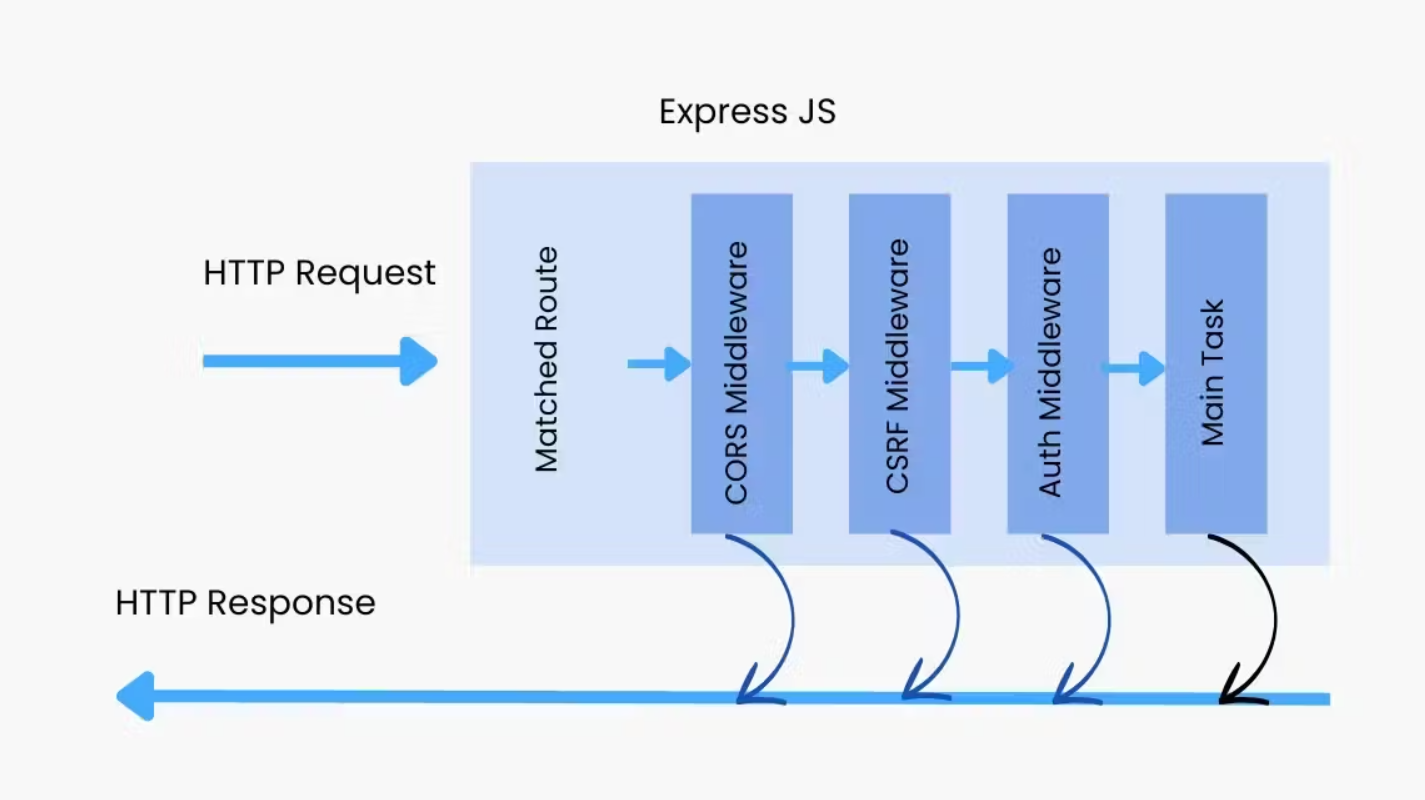
Types of Middleware in Express
There are different types of middleware in Express, each with a specific purpose within an application's flow. The most common are:
- Application Middleware: Applied to the entire application and has access to every incoming request.
- Route Middleware: Applied only to specific routes.
- Error Middleware: Used to capture and handle errors.
Application Middleware
Application middlewares are applied to all routes of the application. They are ideal for global tasks such as request logging, session handling, or the use of CORS.
javascript
Route Middleware
Route middlewares are applied only to a specific route. This allows adding additional functionalities to certain routes without affecting the rest of the application.
javascript
Error Middleware
Error middlewares are special because they are triggered when an error occurs in the application. They have four parameters: err, req, res, and next.
javascript
Creating Custom Middleware
In addition to using predefined or third-party middlewares, we can create our own custom middleware to add specific functionalities to our application.
Example of Custom Middleware for Data Validation
Next, we'll see how to create a custom middleware that validates the input data of a POST request.
javascript
Third-Party Middleware
Besides creating custom middlewares, Express allows using third-party middlewares that add specific functionalities to the application. For example, body-parser is a middleware that allows us to process the request bodies, and cors is used to handle cross-origin security policies.
Installing and Using cors
bash
Then, we configure it as global middleware:
javascript
Middleware for Improving Performance
Another advanced use of middlewares is to optimize an application's performance. We can, for example, implement middleware for HTTP response compression or to cache certain results.
Compression Middleware
The compression middleware allows compressing HTTP responses, which reduces the size of data sent to the client and improves loading times.
Installing compression
bash
Using compression
javascript
Advanced Logging Middleware
In addition to improving performance, we can use middlewares to log detailed information about requests and responses, aiding in application monitoring. We've previously seen how to use Morgan for basic logging, but we can also create more personalized logging middlewares for specific needs.
Custom Middleware for Logging
Here’s an example of how to create a custom middleware that logs the time it takes to process each request:
javascript
Best Practices with Middleware
- Order of Middlewares: The order in which the middlewares are defined is important, as they execute in the same order they were declared. Ensure the most general middlewares are at the beginning and the specific ones at the end.
- Reusing Middlewares: Take advantage of Express's modularity to reuse middlewares in different parts of the application or between projects.
- Avoid Long Processes in Middlewares: Middlewares should be efficient and not block the request lifecycle. If you need to perform heavy operations, consider making them asynchronous or using them in a separate layer.
Conclusion
In this chapter, we've explored the advanced concepts of middleware in Express, including creating custom middlewares, using third-party middlewares, and how to optimize application performance using middlewares. Proper use of middlewares can significantly improve the efficiency and security of an Express application.
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck

- Introduction to Express JS
- Express Fundamentals
- Request and Response Management
- Estructura de Proyectos en Express
- Authentication and Authorization in Express
- Connecting Express with Databases
- Error Handling and Logging in Express
- Sending Emails in Express
- Security in Express Applications
- Advanced Middleware in Express
- Creating REST APIs with Express
- WebSocket Implementation in Express
- Implementation of Webhooks in Express
- Testing Express Applications
- Deployment of Express Applications
- Performance Optimization in Express
- Monitoring and Maintenance of Express Applications
- Best Practices and Scalability in Express
- Course Conclusion: Express JS













