Intermediate React
Complex Component Communication
As React applications grow, communication between components becomes more complex. In this chapter, we will explore various techniques for handling component communication, from passing data from parent to child components to advanced patterns such as lifting state up, prop drilling, and using contexts to simplify application structure.
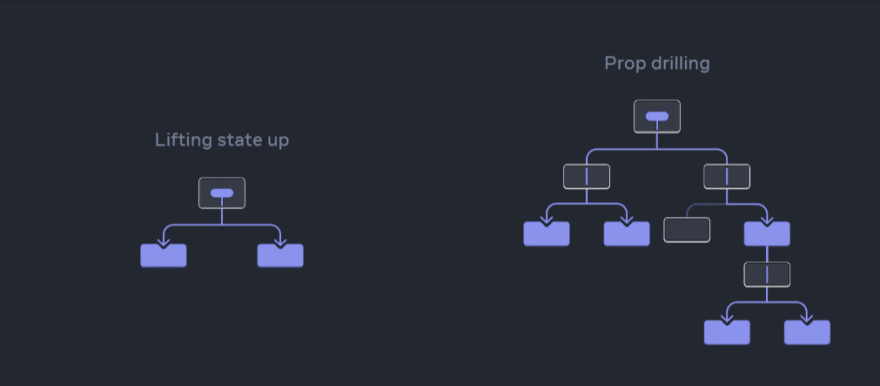 lifting state up and prop drilling
lifting state up and prop drilling
Basic Communication: Passing Props
The most straightforward way to communicate data between components in React is to pass props from a parent component to its children. This is ideal for small applications or when data does not need to be shared across multiple levels of the component hierarchy.
Example of Communication with Props
In this example, the parent component Parent passes data to its child component Child:
javascript
Lifting State Up: Sharing State between Components
Lifting State Up is a pattern that allows sharing state between sibling components. Instead of having state in each component, data is "lifted" to a common component, which then passes the data as props.
Example of Lifting State Up
Here we have two components, Input and Display, sharing the same state:
javascript
Prop Drilling and Its Challenges
When passing information through multiple levels of components, a pattern known as prop drilling occurs. This pattern can become difficult to maintain, especially in large applications where data needs to pass through many components that do not directly use it.
Solution to Prop Drilling: Context API
Context API allows avoiding prop drilling by providing a global state system accessible by any component within the tree. This simplifies data management in complex applications.
Example of Using Context API to Avoid Prop Drilling
In this example, we create a context to share a message without needing prop drilling:
javascript
Advanced Patterns: Events and Callbacks between Unrelated Components
When components do not have a direct relationship in the tree but need to communicate, we can use event emitters or callbacks. In React, this can be handled using function callbacks or subscription patterns.
Example of Communication between Unrelated Components using Callbacks
In this example, two unrelated components share information through a callback function in a parent component:
javascript
Best Practices in Complex Component Communication
- Use Context API for Global State: When multiple components need access to the same data, consider using Context API.
- Avoid Extreme Prop Drilling: Minimize prop drilling to maintain code readability. If possible, use contexts or lift state to a common component.
- Implement Lifting State Up Only When Necessary: Avoid lifting state unnecessarily if not all components need access to the data.
Conclusion
Component communication in React is a crucial aspect for maintaining scalability and maintainability of an application. In this chapter, we explored techniques to efficiently manage data communication, including lifting state up, contexts, and callbacks.
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck

- Advanced State Management with Context API and useReducer
- Performance Optimization in React
- Lazy Loading and Code Splitting
- React Profiler and Performance Analysis
- Context API y State Management Escalable
- Render Props and Higher-Order Components (HOC)
- Error Handling in Components with Error Boundaries
- Refs and Direct DOM Manipulation
- React.memo and useMemo for Performance Improvement
- Suspense Implementation for Data Fetching
- Complex Component Communication
- Advanced Conditional Rendering
- Integration with Animation Libraries
- Advanced Custom Hooks Patterns
- Data Handling and RESTful APIs in React
- Data Caching and Persistence Strategies in React
- Accessibility Management in Interactive Components
- Advanced Performance Optimization in React
- Testing Components with Mocking and Integration Tests
- Best Practices in React Component Architecture
- Creation of Reusable React Components
- Conclusions and Next Steps in Advanced React













