Intermediate React
Data Handling and RESTful APIs in React
In most modern applications, it is common for data to be retrieved and sent through a RESTful API. React provides tools and patterns for handling data loading, updating, and storage in interactive interfaces. In this chapter, we will explore how to integrate RESTful APIs in React applications, including request handling, state storage, and optimization strategies.
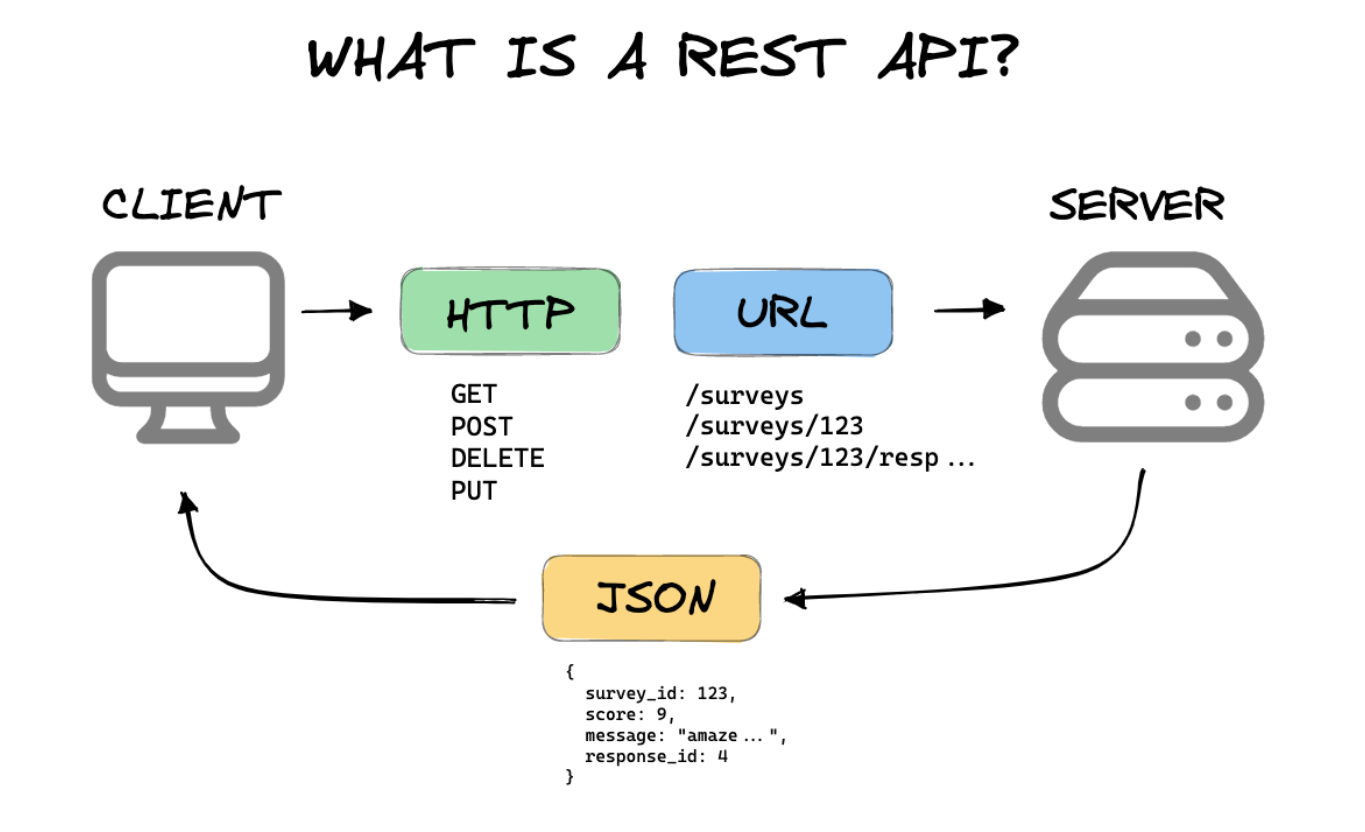
Introduction to API Requests in React
API requests are commonly made using the fetch method or with libraries like Axios to retrieve data from external servers. This data can be stored in a component's local state or in a global state to be accessible throughout the application.
Basic Request Example with Fetch
In this example, we use fetch to make a GET request to an API and store the data in the state:
javascript
Using Axios to Simplify Requests
Axios is a popular library for making HTTP requests that provides more concise syntax and additional configurations compared to fetch. Its use simplifies error handling and sending custom headers.
Example with Axios
Below, we show how to use Axios to retrieve data from an API:
javascript
Optimizing Requests with useEffect and Dependencies
When using useEffect for data requests, it's essential to manage dependencies correctly to avoid multiple unnecessary requests. Additionally, we should consider cleaning up effects to avoid state conflicts.
Optimization Example with Dependencies
In this example, we avoid requesting data multiple times by updating only when userId changes:
javascript
Controlling Global State with Context API and Reducers
To handle data retrieved from an API throughout the application, we can combine Context API with useReducer. This allows storing and updating the global data state needed by multiple components.
Global State Example for User Data
Here, we create a context and a reducer to manage the user state throughout the application:
javascript
Best Practices for Data Handling and APIs in React
- Limit Duplicate Requests: Optimize effects and their dependencies to avoid multiple requests to the same API.
- Use Data Management Libraries: Libraries like Axios and React Query simplify data handling and offer additional features to enhance efficiency.
- Implement Context for Global Data: Use Context API for data that needs to be accessible across various components in the application.
Conclusion
Data handling and integrating RESTful APIs in React are essential skills for building interactive and scalable applications. In this chapter, we explored how to perform data requests, manage local and global state, and optimize data loading in React applications.
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck

- Advanced State Management with Context API and useReducer
- Performance Optimization in React
- Lazy Loading and Code Splitting
- React Profiler and Performance Analysis
- Context API y State Management Escalable
- Render Props and Higher-Order Components (HOC)
- Error Handling in Components with Error Boundaries
- Refs and Direct DOM Manipulation
- React.memo and useMemo for Performance Improvement
- Suspense Implementation for Data Fetching
- Complex Component Communication
- Advanced Conditional Rendering
- Integration with Animation Libraries
- Advanced Custom Hooks Patterns
- Data Handling and RESTful APIs in React
- Data Caching and Persistence Strategies in React
- Accessibility Management in Interactive Components
- Advanced Performance Optimization in React
- Testing Components with Mocking and Integration Tests
- Best Practices in React Component Architecture
- Creation of Reusable React Components
- Conclusions and Next Steps in Advanced React













