Basic React
Advanced State Management
State management is one of the most critical aspects of any React application. As applications grow, state management can become more complex, especially when multiple components need to access the same state or when the state must be shared globally. In this chapter, we will explore advanced techniques for managing state in React, including the Context API and Redux.
Context API vs Redux
Both the Context API and Redux are popular solutions for global state management in React. The Context API is a built-in tool in React that allows state sharing between multiple components without prop drilling. On the other hand, Redux is an external library that offers a more structured and scalable architecture for handling complex states.
When to Use the Context API
The Context API is ideal for managing states that need to be shared in a specific part of the application, such as UI themes, authenticated user data, or global configurations. It is simple to set up and is a native part of React, making it an excellent choice for small to medium applications.
When to Use Redux
Redux is more suitable for larger and more complex applications that require more robust and predictable state management. By separating the state and update logic into "reducers," Redux makes it easier to debug and scale complex applications.
Using the Context API
The Context API allows you to create a global context that any component can access without manually passing props. This is useful when you need to share data like user authentication or theme settings.
Creating a Context
The first step is to create a context using createContext:
jsx
The ThemeContext.Provider component wraps the rest of the application and provides the context value (theme and setTheme) to all components inside it.
Consuming the Context
Components that need to access the context values can use the useContext hook:
jsx
Here, the Toolbar component accesses the current theme and the setTheme function from the context. This allows the user to change the theme without manually passing props to each component.
Using Redux
Redux follows the Flux architectural pattern and provides a centralized way to manage the application's state. Although it requires more setup than the Context API, it offers a more scalable structure for large applications.
Installing Redux
First, you need to install redux and react-redux, which are the libraries needed to integrate Redux into a React application:
bash
Creating a Redux Store
Global state in Redux is managed through a store, which is a container for the entire application's state. The first step to using Redux is creating a store:
jsx
In this example, we create a store using createStore and provide the global state through the Provider component. The counterReducer reducer handles the actions to increment and decrement the counter.
Connecting Components to Redux
To access the Redux state in components, you can use the useSelector hook to get the state and the useDispatch hook to dispatch actions that update the state.
jsx
Here, the Counter component accesses the counter state using useSelector and dispatches actions to increment or decrement it using useDispatch.
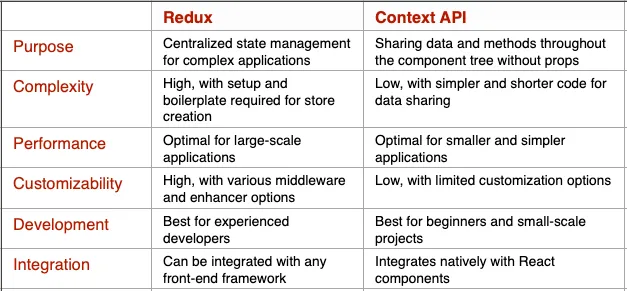
Comparison between Context API and Redux
| Feature | Context API | Redux | |-----------------------------|-----------------------------------|----------------------------------| | Scalability | Ideal for small applications | Better for large applications | | Configuration | Simple and quick | More complex | | State Management | For sharing simple data | Ideal for complex states | | DevTools and Debugging | No dedicated tools | Offers Redux DevTools |
Both solutions have their place depending on the complexity of the application. If you only need to share some simple data between components, the Context API is an excellent choice. For larger applications with complex logic, Redux provides a more robust structure.
Conclusion
Both the Context API and Redux are powerful tools for managing global state in React. Each has its advantages and fits different types of applications.
Support Chuck’s Academy!
Enjoying this course? I put a lot of effort into making programming education free and accessible. If you found this helpful, consider buying me a coffee to support future lessons. Every contribution helps keep this academy running! ☕🚀

Chat with Chuck

- Introduction to React
- JSX Fundamentals
- Functional Components in React
- State and Lifecycle with Hooks
- Event Handling in React
- Communication between Components
- Conditional Rendering and Lists
- Forms and Input Handling in React
- Styles in React
- React Router: Navigation in Applications
- Advanced State Management
- Performance Optimization in React
- Creating Custom Hooks in React
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR) en React
- Handling APIs and Fetch in React
- Using GraphQL with React
- Testing in React
- Introduction to Class Components
- Third-Party Components and Useful Libraries
- Integration with WebSockets
- Gestión de Archivos y Subidas en React
- Deployment of React Applications
- Best Practices and Patterns in React
- Conclusions and Next Steps













